Code Coverage
How many lines of your code are covered by automated tests? Did you miss any by accident? Use Code Coverage to check it out!
What Is a Code Coverage
Code Coverage (CC) measures how many, and which specific source code lines are being tested by automated tests (for example, unit or integration test). If you have 90% CC, it means that 10% of the source code is not being tested at the moment. Your goal is to get as close to 100% CC as possible without losing the quality of your code or tests. CC can be used as a key performance indicator for suppliers. The tests should be run by developers, they should not rely only on Continuous Integration.
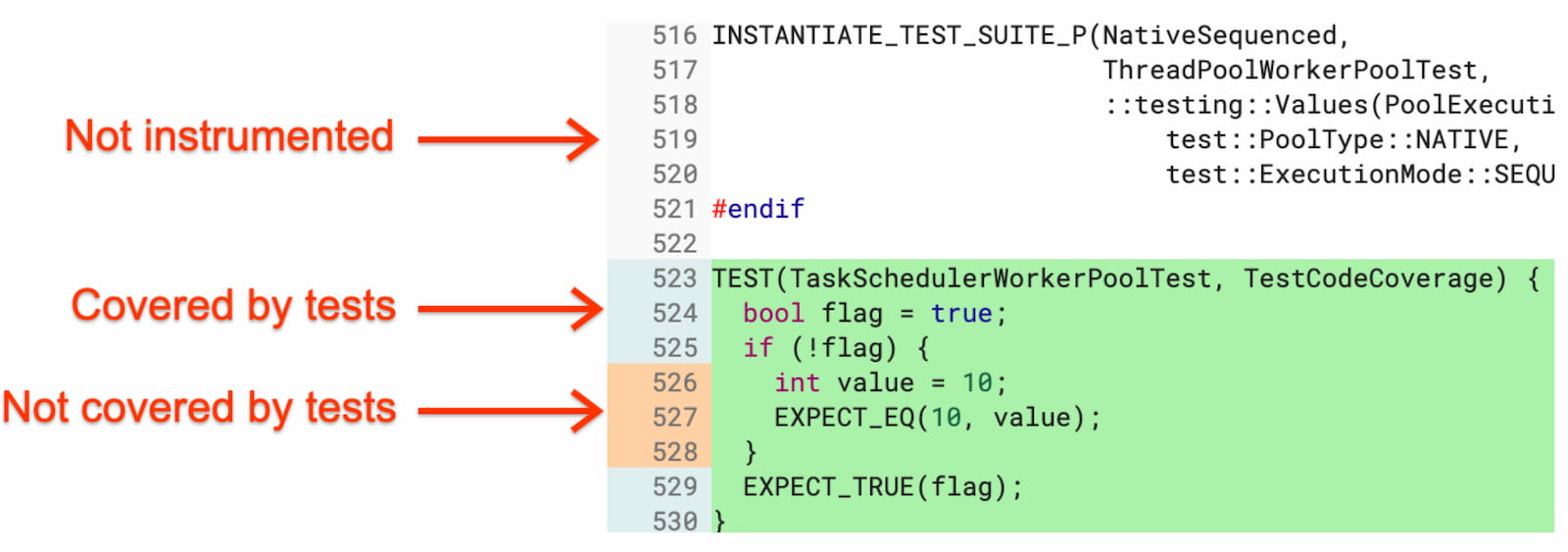 Source: Developers.google.com: The Chromium Chronicle: Code Coverage in Gerrit
Source: Developers.google.com: The Chromium Chronicle: Code Coverage in Gerrit
CC is usually calculated in a Continuous Integration library, for example, GitLab. This library opens an application that measures the CC automatically. The library provides you with coverage reports, for example:
- Function coverage: How many defined functions have been called.
- Statement coverage: How many statements in the program have been executed.
- Branches coverage: How many control branches structures have been executed.
- Condition coverage: How many boolean sub-expressions have been tested for a true and a false value.
- Line coverage: How many lines of source code have been tested.
Why You Might Want Code Coverage
- The coverage reports are great feedback - they can provide CC for every file.
- The tools for CC are often open source tools so you can see the quality of the library.
- CC can be used for measuring the quality of supplies and services.
- CC can reveal major mistakes during early software phases (building or compiling). It can serve as a Smoke Test.
- In order to get official certification, some software is required to use CC. CC is mandatory, for example, for air and space transportation, rail transportation, the automotive industry, or for medical applications.
Problems the Code Coverage Solves
- Poor code quality
- Unsuccessful product
- Unhappy clients
- Disconnect Between Business and IT
- "Not my problem" mentality
- Meaningless work
How to Implement the Code Coverage
Set up the library for your software and run it under a controlled environment. Use a CC tool to map every executed function.
There are a lot of CC tools you can use, for each programming language. For example:
- Java: jUnit, Cobertura, or JaCoCo
- JavaScript: istanbul, or JSCover
- PHP: Clover, or PHPUnit
- Python: coverage.py
- Ruby: SimpleCov
- Scala: Scoverage
Update the tests if there are no areas of code that have not been exercised. Developers can check CC reports to advise additional tests to increase the CC. Important: The process can slow down the application so it is not recommended to do it in production.
Common Pitfalls of the Code Coverage
- Developers write useless tests to reach 100% CC.
- A developer corrects the functionality but does not correct the test. That means that a wrong test can fool the CC.
- A deveoper writes new code and applies wrong tests. The CC declines.
Resources for the Code Coverage
- Microsoft: Use Code Coverage To Determine How Much Code Is Being Tested
- Atlassian: Code Coverage
- Innominds: How Does Code Coverage Help In Testing?
- Jeroen Mols: The 100% Code Coverage Problem
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Penetration Testing
Penetration Tests are performed to identify network security weaknesses. It is a "friendly cyberattack" for spotting flaws and potential vulnerabilities.
Read moreCode Review
Code Review is an important practice for checking each other's code. The reviewers are other developers from the team. The goal is to uncover potential mistakes that could slip through testing.
Read moreProper Bug Reporting
Proper bug reporting is a crucial practice for development. It helps to understand where the product lacks its functionality or performance. Bug reports are descriptions of bugs found by testers.
Read moreSmoke Testing
It is a test aimed to verify that the most important features of the product really work. This term was used during testing hardware and the product passed the test when it did not burn or smoke.
Read moreContinuous Integration
Continuous Integration is a software development practice that makes developers integrate code changes into a shared repository routinely and frequently. Usually, each person integrates at least daily and that ensures them that their code changes do not break anything.
Read moreALL ARTICLES