REST API
The majority of applications in use today are created for web and mobile platforms. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for the web have consequently gained importance. Among the different types of web APIs, REST (Representational State Transfer) API has become the most popular due to its simplicity, scalability, and flexibility.
What is an API
There have been a lot of definitions of API from industry leaders, after going through these numerous definitions I can simply describe APIs as a state of mechanisms that enable two software components to communicate with each other using a set of definitions and protocols.
According to Mastering API Architecture book by James Gough, Daniel Bryant & Matthew Auburn describe API as:
- An API represents an abstraction of the underlying implementation.
- An API is represented by a specification that introduces types. Developers can understand the specifications and use tooling to generate code in multiple languages to implement an API consumer (software that consumes an API).
- An API has defined semantics or behavior to model the exchange of information effectively.
- Effective API design enables the extension to customers or third parties for business integration.
What is the REST API?
A set of constraints to be applied while developing web services are defined by the REST architectural style for software. In general, REST technology is favored above other, comparable technologies. This is frequently the case as REST requires less bandwidth and is therefore more suited for effective internet use.
A RESTful API is based on representational state transfer (REST), an architectural style and approach to communications that is frequently used in the building of web services. It is also known as a RESTful web service or REST API. RESTful APIs are also referred to as web services.
Safe online information exchange between two computer systems is made possible by the RESTful API. To carry out various duties, the majority of business apps must interface with other internal and external applications. For instance, in order to automate invoicing and connect with an internal timesheet application, your internal accounts system must exchange information with your customers' banking system in order to generate monthly payslips. This information transmission is supported by RESTful APIs because they adhere to standards for safe, dependable, and effective software communication
Why You Might Want the REST API
REST APIs are crucial for businesses because of the advantages they provide. In the end, what matters is how the APIs are generating income for the company.
-
Business value REST API can benefit the company's partners, internal team, and external team. APIs are utilized to interchange data and functionality. Amazon has numerous number of product and services and still need these individual products to sync and communicate with each other, APIs are used to exchange data & functionality. For Partner, the Twitter API enables third-party programs to read from and write to Twitter data. It allows you to create and post tweets, share tweets, and read profiles. This API is useful for collecting and reviewing huge numbers of tweets about specific topics. It is either the company generates income by making its API available to the public or by using them to create its own product.
-
Cost Benefits Using/Building REST APIs has a positive impact on costs. They provide scalability without the need for costly hardware investments, improve team communication through improved performance, reduce costs by supporting several platforms, and save time. Hence, if you're going to spend money on software applications for your company, be sure that your development team relies heavily on REST APIs.
-
Performance The lightweight nature of REST APIs means that much fewer data needs to be transmitted from server to client. Applications that use REST APIs as their foundation operate more effectively.
Problems the REST API Helps to Solve
As a popular architectural style for designing and developing web-based APIs. It helps to solve a variety of problems related to building web-based applications and services, including:
- Scalability RESTful APIs are highly scalable due to their stateless nature, which allows for easy scaling of resources.
- Flexibility RESTful APIs are flexible in terms of the format of data, which allows for easy integration with other web-based systems.
- Easy to understand RESTful APIs are easy to understand due to their simplicity and uniform interface.
- Easy to develop RESTful APIs are easy to develop due to their uniform interface and stateless nature, which reduces the complexity of the application.
- Platform independence RESTful APIs can be used with any programming language and platform, making them highly interoperable.
How to Implement RESTful API
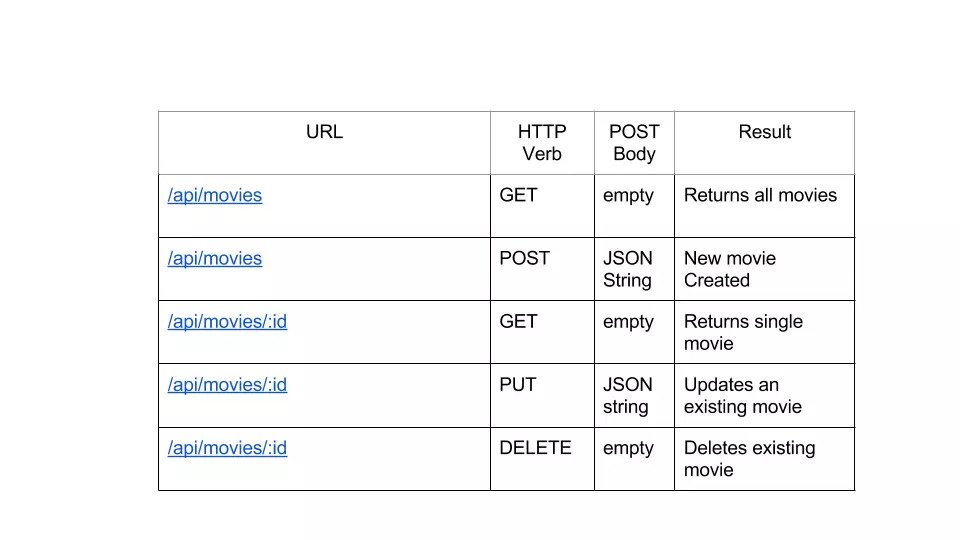 Source: Sitepoint: RESTful API
Source: Sitepoint: RESTful API
A RESTful API uses commands to obtain resources. In REST, each resource is identified by a unique URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) and can be manipulated using standard HTTP methods as defined by the RFC 2616 protocol, such as:
- GET to retrieve a resource;
- PUT to change the state of or update a resource, which can be an object, file or block;
- POST to create that resource; and
- DELETE to remove it.
It is based on the idea that the REST APIs are stateless, meaning that calls can be made independently of one another, and each call contains all of the data necessary to complete itself successfully
The core principles of RESTful API The principles of REST are centered around a few core concepts, which include:
-
Stateless communication RESTful APIs should be stateless, meaning that no client context should be stored on the server between requests. Each request should contain all the necessary information to complete that request, including authentication credentials if required.
-
Resource identification Resources should be identified using unique URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) that are included in the request. Each resource should have a unique URI, and requests should use these URIs to manipulate the resource.
-
Uniform interface A uniform interface should be used to access resources. This means that HTTP methods should be used to access resources, and the same HTTP method should have the same effect on all resources.
-
Representation of resources Resources should be represented in a format that is easily consumable by the client. This can include JSON, XML, or other formats.
-
Hypermedia as the engine of application state (HATEOAS) This principle states that the client should be able to navigate the API using hyperlinks included in the response. This allows the API to evolve without breaking existing clients.
Common Pitfalls of the REST API
-
Embrace Versioning Accept versioning because your company will change, as will your processes and what customers desire. But, because of this ongoing, unavoidable change, it is necessary to initially design versioning techniques and provide answers to queries like how frequently you plan to version your API.
-
API design It doesn’t end at the business giving value through its API, You must take into account the developer experience(DX) in addition to the business providing value through its API. Just adhere to the established practices to create excellent APIs and DX.
-
Be consistent with the HTTP status code, proper names (nouns), and industry standards
-
To obtain data, use GETs.
-
To change data, use PUTs and POSTs.
-
Consistently use the same overall endpoint structure.
-
Choose a few reliable status codes and make sure to appropriately and consistently apply them throughout your API.
Resources for the REST API
- GeeksforGeeks: Why RESTful API is important to learn
- TechTarget: When REST API protocols do from helpful to harmful
- Knowledgehut: What is Rest API? Features, Principles, And Challenges
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
API-First Development
API-first approach to building products is rising, API first enables developers to innovate in ways that weren't before feasible and speed up the achievement of corporate goals.
Read moreDeveloper Portal
A Developer Portal is a centralized online platform that equips developers with tools, documentation, and resources to efficiently use and integrate APIs or SDKs provided by a company, fostering collaboration and a seamless developer experience.
Read moreALL ARTICLES