Kanban
Learn about a famous agile method with a Japanese name Kanban. It helps your team to concentrate on finishing their tasks and to avoid the "bottleneck effect".
What Is Kanban
Kanban is an agile method similar to Scrum but it is less structured (no specific timeframe) and it is based on a list of items to do. It is focused on managing a continuous delivery of products with avoiding the "bottleneck effect" that may cause overloading of the team. The term Kanban comes from Japan world "Kan" and it means visual or visible. A "Ban" is a card or board. As the name suggests, it is a visual system - you can use an actual board and sticky notes to create a picture of your work. Create three columns: "to-do", "doing", and "done" and move your sticky notes accordingly.
Kanban is summarized by the premise: "Stop Starting, Start Finishing". Teams concentrate on getting to the "done" status the issues that are "in progress".
Why You Might Want Kanban
- Kanban is flexible to the changes and ideal when priorities change very frequently.
- Kanban requires only a few organization or room set-up changes and costs to get started.
- Kanban helps to reduce waste. It encourages removing activities that do not add value to the team/department/organization
- Rapid feedback loops and better access to information affect positively team members. They are more motivated, empowered and higher-performing.
- In comparison with the Waterfall methodology, Kanban brings faster delivery of features thanks to shorter cycle times.
- Compared to Scrum, Kanban uses fewer meetings and supporting processes. For example, there is no need for any control measures such as velocity.
Problems the Kanban Helps to Solve
- Demotivated team
- Increased cost
- Bad product-market fit
- Meaningless work
- "Not my problem" mentality
- Unhappy Clients
- Toxic team culture
- Disconnect Between Business and IT
How to Implement Kanban
Kanban is based on the following key principles:
- Visualize a workflow Kanban board is a visualization mechanism and presents what the team does today. Either use an actual board and sticky notes or use one of various templates, such as Trello, MeisterTask, or Kanban Tool. Set your process steps considering the complexity of your project.
- Limit of work in progress (WIP) Teams do not start too many work issues at once. It helps to keep the workflow in the balance.
- Manage workflow The typical Kanban practice is also explicit policies, such as WIP limits, acceptance criteria, or clear definition of the flow. For example, when something is finished, the next highest item from the backlog will be picked out.
In addition, Kanban encourages collaboratively improving, experimental evolving, and constant learning by feedback loops.
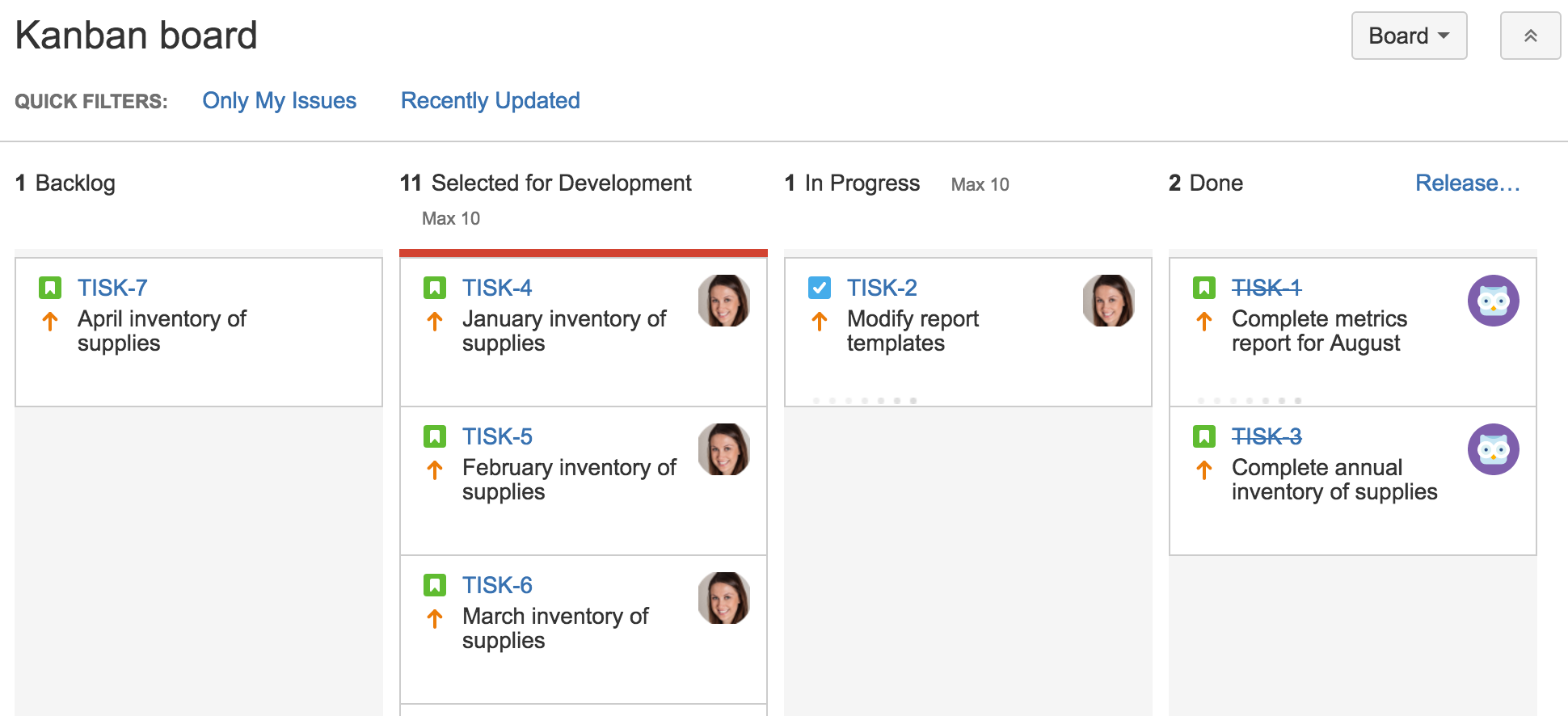 Source: Learn Kanban with Jira Software
Source: Learn Kanban with Jira Software
Common Pitfalls of Kanban
- "Big Bang" The approach of starting everything from zero may cause you a lot of trouble. Kanban is about continuous enhancement. So, instead of throwing your current process away, map it on a Kanban board and start improving.
- Nobody respects the WIP limits It caused that the Kanban board is overcrowded at each stage of the workflow and issues are moving very slowly to "done" column. Applying WIP limits and respecting them ensure that team members are focused on their current work and process runs faster. Keep in mind that applying WIP limits may not work from the very first try. You need to monitor your workflow constantly and adjust WIP limits until you find the optimal configuration for your team. Tip: There are many approaches for setting initial WIP limits, for example, "two items per person", "start with the number what you do now", or "n-1" (setting one under the number of team members may cause greater collaboration by forcing team members to work together).
- Nobody respects the Kanban board Problems appear directly to "done" stage without being picked out from the backlog and going through the workflow. Do not forget, the purpose of a Kanban board is a visualization of everything the team does. It helps to estimate the team’s capacity and utilize them to their maximum level.
- Focus On Tools In brief, tools are not important - people and principles are.
Resources for Kanban
- Collab: What Is Kanban? An Introduction to Kanban Methodology
- Sitepoint: How & Why to Use the Kanban Methodology for Software Development
- Agile Alliance: Kanban
- Proof Hub Blog: What Are the Advantages of Kanban Board System
- Kanbanize: 6 Reasons you May Fail with Kanban Implementation
- Excella: How to Set Initial WIP Limits
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Devops
DevOps is a set of practices that brings development and operations teams together. The collaboration helps to release software much faster.
Read moreRelease Management
Release management is the process of managing, planning, designing, scheduling, testing, controlling and deploying of a software build through different stages and environments; in preparation for software releases.
Read moreAgile Events
Agile Events are necessary meetings for keeping up the good work. They are usually time-boxed and the most common Agile framework that uses these periodic rituals is Scrum.
Read moreCode Review
Code Review is an important practice for checking each other's code. The reviewers are other developers from the team. The goal is to uncover potential mistakes that could slip through testing.
Read moreScrum
Scrum is an agile framework focused on a productive and creative delivery of complex products with an emphasis on the highest possible value. Scrum is lightweight, simple to understand and difficult to master.
Read moreALL ARTICLES