Design Sprint
Create and test your prototype in just 3 - 5 days! Learn how to reduce the risk when creating a new product with five simple steps.
What Is a Design Sprint
The Design Sprint is a five-phase process to get a tangible product prototype in a short period of time. This tool helps to describe the product’s benefits, reach the challenge, gain key learnings, and get the product validation by user testing in just 3 to 5 days. The Design Sprint process is similar to Sprints in an Agile development cycle.
The Design Sprint uses design thinking to reduce risks of launching a new product, service or a feature. It is a unique way how to get the feedback without going the full cycle.
 Source: Wikipedia.org - Design Sprint
Source: Wikipedia.org - Design Sprint
Phases of the Design Sprint:
-
Map Map the problems and identify the important areas to focus on. Set a long term goal.
-
Sketch Sketch down the creative ways how to solve the problem on the paper.
-
Decide Remove the unfeasible ideas from the first two phases. Make a storyboard and decide what should be prototyped. The final choice is made by Decision Makers.
-
Prototype Make a realistic prototype that can be tested by potential or existing customers.
-
Test Run the user testing and get the feedback.
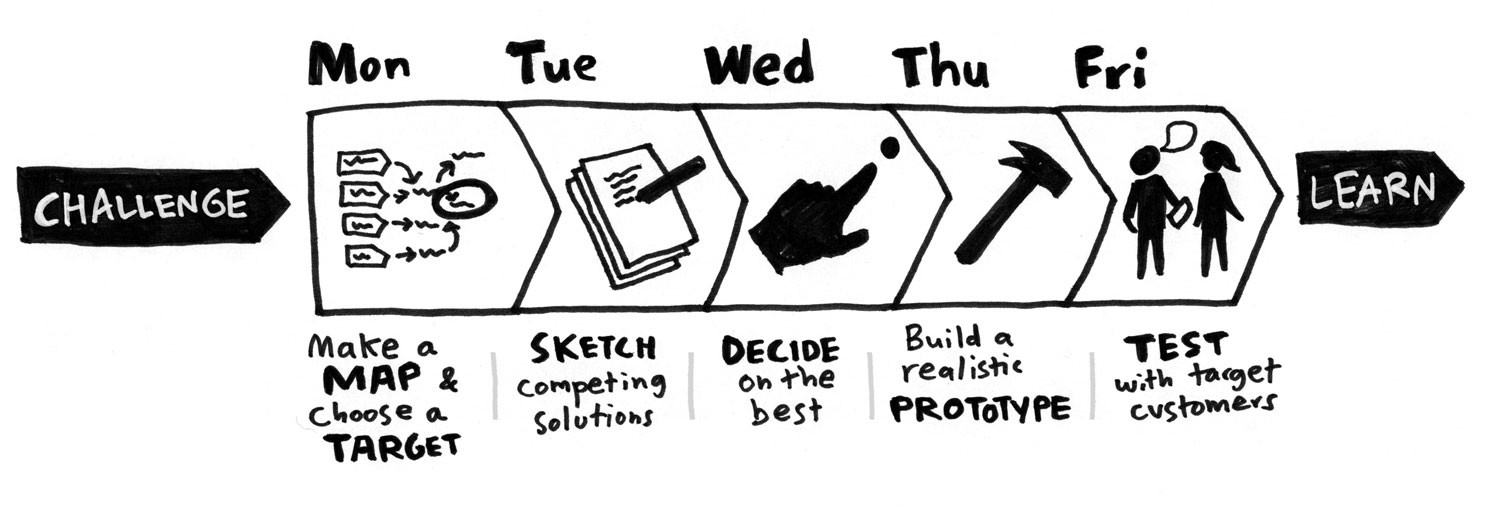 Source: What’s a Design Sprint and why is it important?
Source: What’s a Design Sprint and why is it important?
Why You Might Want the Design Sprint
The Design Sprint process helps to:
- assure the team that they are heading in the right direction.
- understand the visions and risks. It enables the team to see the world through the customer's eyes.
- empower every member of the team to contribute to the project.
- save time. The number of meetings is significantly reduced.
- save the money. The team avoids unknowns or assumptions as long as they understand the risks.
Problems the Design Sprint Solves
- Demotivated team
- Increased cost
- Bad product-market fit
- Meaningless work
- "Not my problem" mentality
- Unhappy client
- Toxic team culture
- Disconnect Between Business and IT
How to Implement the Design Sprint
Make a team. The ideal number of people involved in the sprint is 4 to 7. The team includes a Facilitator, a Designer, a Decision Maker, a Product Manager, an Engineer, and someone from companies core business departments (for example, Marketing, Content, or Operations).
The Facilitator manages the sprint. A good Facilitator leads the meetings and encourages the team to share their ideas and find the solutions. It is mostly a silent or unbiased role in group discussions.
The Decision Maker (or the Decider) has the ultimate authority to select what goes into the prototype. This role is often played by the company’s CEO or by someone with the budget authority. The Design Sprint is just the first step in product development. The team needs a powerful decider to pursue the product after the Design Sprint and until the implementation.
The preparation is very important:
- Find a good Facilitator.
- Define the challenge (not too vague).
- Block out the entire week for the whole team.
- Book a room. Forbid anything that could distract the team from focusing (for example, mobile phones).
- Distribute enough post-it notes, ensure there is a whiteboard in the room and enough markers.
- Follow the five-step process from above.
Ensure that everyone understands what they should do during the first two phases (assign homework so they can prepare by themselves). Collect and store everything from the room (for example, collect the post-it notes, take photos of the whiteboard, etc.).
Common Pitfalls of the Design Sprint
- The Design Sprint is commonly mistaken with a workshop.
- It is necessary to clearly define experts and targets.
- It is important to make the goal broad enough but not too vague so that the team has enough room for coming up with new ideas.
- The decision maker should be able to suppress their ego.
Resources for the Design Sprint
- The Sprint book
- Thoughtbot: The Product Design Sprint
- InVision: The Design Sprint
- GV: The Design Sprint
- Google Products: The Design Sprints
- UX Planet: What’s a Design Sprint and why is it important?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Lean Canvas
A Lean Canvas is a 1-page chart with 9 basic building blocks. It helps to identify problems and solutions for your product.
Read moreFail Fast
Fail Fast is a method used during a recurrent approach to determine whether an idea has a value for the client or solution. An important goal is to minimize losses when testing reveals something is not working and quickly try something else.
Read moreClickable Prototype
Clickable Prototypes are interactive demos of a website or a software application. These are often used to gather feedback early in the project lifecycle, before the project goes into the final stage of development.
Read moreAgile Events
Agile Events are necessary meetings for keeping up the good work. They are usually time-boxed and the most common Agile framework that uses these periodic rituals is Scrum.
Read moreValue Proposition
A Value Proposition Canvas is a model that helps to ensure that a product covers customer’s requirements. It defines the customer segment and the value proposition.
Read moreALL ARTICLES